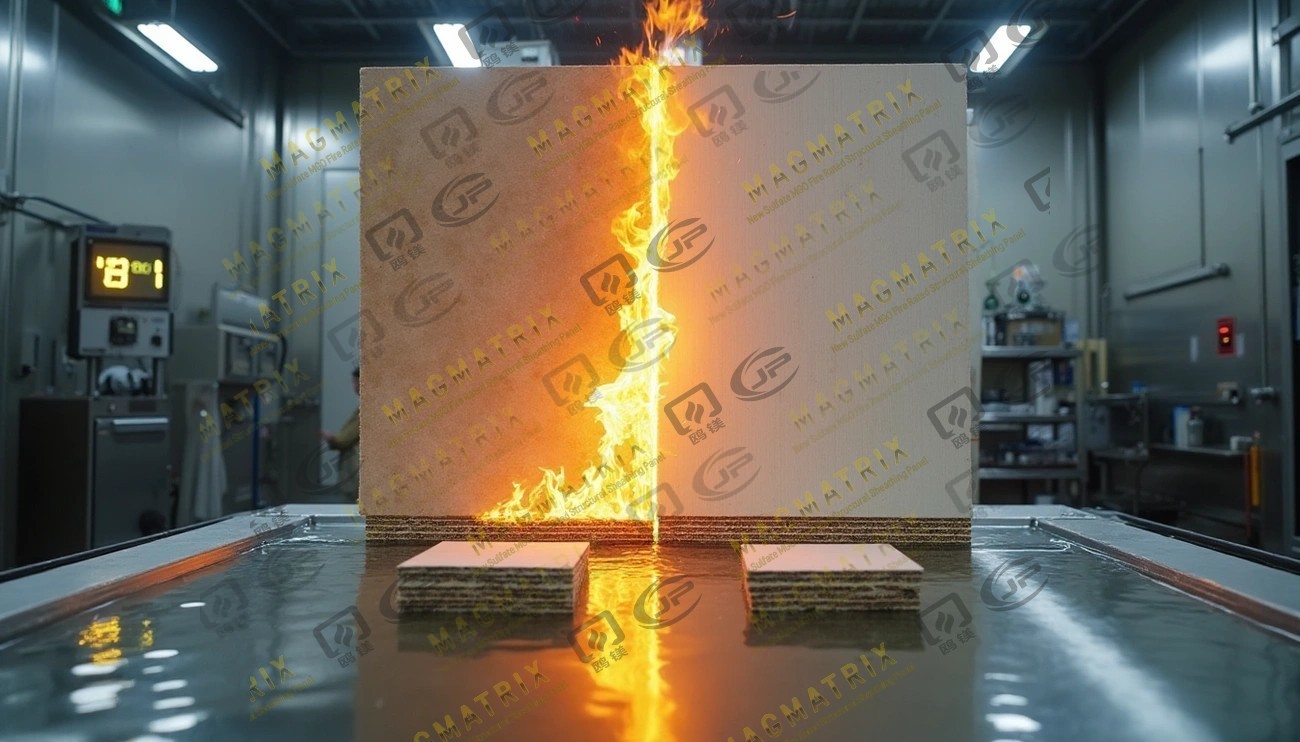
MgO board is a remarkable building material that can handle temperatures up to 780°C (1436°F) without burning or creating smoke. Builders are choosing MgO boards more often than traditional floor sheathing options because of this amazing fire resistance.
These magnesium oxide panels have a flame-spread index of zero, which means they don't help fires spread at all. On top of that, they're incredibly tough in harsh conditions and absorb less than 15% water even after two-hour immersion tests. MgO is harder and stronger than drywall, and it fights off insects, mold, mildew, and rot better too. Tests on more than 1,000 samples over two years show that magnesium oxide sheathing stays stable even when wet.
The price tag might be higher at first compared to traditional options, but MgO boards save money over time through less maintenance and a longer life. In this piece, we'll get into the test results that show why MgO board technology is the future for construction professionals who want better performance and safety.
Material Composition of MgO vs Traditional Sheathing
MgO boards get their structural strength and great performance mainly because of their unique chemical makeup and how they're made. These basic differences explain why MgO boards work better than regular options in tough applications.
Magnesium Oxide Panel Composition: MgO, Perlite, Fiberglass Mesh
Today's magnesium oxide panels use a carefully crafted mix of minerals and reinforcing materials. The core has 56-58% magnesium oxide (MgO), which makes it incredibly strong and fire-resistant. This main ingredient works with either 27-29% magnesium sulfate binds everything together.
The other key parts are:
3-4% perlite: This volcanic glass expands with heat and makes the board fire-resistant and insulating while staying lightweight
4-6% fiberglass mesh: This boosts strength, stops cracks, and keeps the board stable under pressure
5-6% wood fiber: Less shrinkage and easier handling during building
0.1-0.3% phosphate: This keeps the chemical matrix stable within the hydration reaction process
These minerals create a cement-like material that lasts incredibly long. The board's amazing strength comes from strong atomic bonds between magnesium and oxygen that create magnesium oxide crystals.
Plywood and OSB Core Layers and Adhesives
Regular floor materials like plywood and oriented strand board (OSB) are quite different in their composition and manufacturing process. OSB uses wood strands stuck together with strong glues, layered in crossing patterns. This cross-layering makes it strong, but doesn't give it the natural fire resistance that mineral-based panels have.
The glues used in wood-based panels show some key differences:
Phenol formaldehyde (PF): This was the go-to glue for OSB, but manufacturers now use other options more often
Methylene diphenyl di-isocyanate (MDI): European makers love this one because it bonds well with wood's hydroxyl groups
Melamine-urea-phenol-formaldehyde (MUPF): Another common choice that handles moisture pretty well
The amount of glue makes a big difference in how well these boards work. Research shows that doubling the glue from 3% to 6% makes OSB boards much better at handling water and staying strong. But even these improved boards can't match how well MgO boards handle extreme conditions.
Moisture-Resistant Magnesium Sulfate vs Chloride Formulations
MgO board technology took a big leap forward when manufacturers switched binding agents. They moved from magnesium chloride (MgCl₂) to magnesium sulfate (MgSO₄), and this change made the boards work much better.
Magnesium chloride boards have some tough problems:
They soak up too much moisture from the air
About 5% of their chloride content can dissolve, which leads to rust
They can "weep," with moisture building up on their surface
Metal fasteners might rust because of moving chloride ions
The newer magnesium sulfate boards fix these issues:
Only about 1% of their chloride content can dissolve
They don't soak up nearly as much moisture
Water resistance is much better
No more weeping or white crystal buildup
The chemistry explains why these boards work so differently. Magnesium sulfate stops moisture from getting back into the board's halogen, which creates a more stable structure that is less reactive.
This change in ingredients marks a huge step forward. Modern MgSO₄-based magnesium oxide boards work much better in tough conditions than both wood-based materials and older MgO boards.
Fire Resistance Test Results and Safety Ratings
Fire testing shows big differences between building materials. These tests explain why magnesium oxide boards work better in safety-critical uses. Lab tests give clear measurements to calculate these performance gaps through standard testing methods.
ASTM E136 Failure Threshold: 780°C
ASTM E136 test measures if a material can burn or not. The test puts material samples in a vertical tube furnace at 750°C (1382°F) for at least 30 minutes. Materials pass this tough test only if they stay below 780°C (1436°F).
MgO panels perform differently based on their makeup. Tests by independent labs in 2020 showed that many leading US market MgO structural panels failed the ASTM E136 test. These samples hit temperatures way above the 780°C limit.
Total Organic Carbon (TOC) content seems to decide if a material passes this test. ASTM E136 Commentary Section X1.5.1.1 states that building materials with 3% or more combustible material often fail the non-combustibility test. The tested MgO panels had TOC levels from 3.61% to 7.29%, which led to their failure.
Flame Spread Index: MgO = 0 vs Plywood = High
The Steiner Tunnel Test (ASTM E84) measures the rate at which fire spreads across materials. This test gives us the Flame Spread Index (FSI).
Quality magnesium oxide boards shine in this test:
| Material |
Flame Spread Rating |
Smoke Development |
| MgO Board |
0 |
0 |
| Plywood |
High (untreated) |
High |
| Drywall |
Higher than MgO |
Moderate |
Zero flame spread rating means MgO boards don't catch fire or help fires spread. Standard plywood catches fire easily and helps fires grow faster in buildings. Even plywood treated with fire-retardants can't match properly made MgO boards.
4-Hour Fire Rating in ASTM E119 for MgO Boards
ASTM E119 (also called ANSI-UL 263) tests how entire wall systems handle fire. Materials face a controlled fire reaching over 1600°F (870°C).
Fire resistance ratings tell us how long walls stay strong during fires. These ratings affect building codes and people's safety.
Quality magnesium oxide boards excel here too:
Up to a 4-hour fire rating in proper setups
Meet ISO 9151, ISO 15025, and ISO 6942 standards
Stay strong even at temperatures near 1200°C (2192°F)
MgO-based walls give people more time to escape than traditional materials. Standard plywood lasts only 30 minutes before breaking down. MgO boards stay strong for up to four hours, eight times longer.
MgO boards stay strong in extreme heat because they char and soak up heat instead of burning. This gives people more time to escape and firefighters more time to work.
These results prove that well-made magnesium oxide boards protect better against fire than regular floor materials. They're a great choice when fire safety matters most.
Water Absorption and Mold Resistance Under Lab Conditions
Lab tests show why magnesium oxide boards keep their structure intact in wet environments where regular sheathing fails. These tests prove why MgO panels are becoming the go-to choice for tough applications.
0.34% Water Absorption in 2-Hour Immersion Test
A building material's water resistance depends heavily on its surface moisture absorption rate. MgO boards shine in this area - they absorb just 0.34% water by weight. This tiny absorption rate explains why these panels stay stable even after long exposure to moisture.
The numbers tell a clear story when compared to other materials:
| Material |
Surface Moisture Absorption |
| MgO Board |
0.0034 |
| Calcium Silicate |
0.03 |
| Gypsum Board |
<citation index="21" link="https://sulfycor.com/mgo-board-mold-resistant-vs-gypsum-board/" similar_text="Here’s a simple comparison of mold resistance: Feature |
| Plywood/OSB |
Over 20% |
High-quality magnesium oxide sheathing absorbs less than 10% water by mass during standard two-hour tests. These boards match gypsum panels in controlled conditions and outperform wood-based options that soak up 20% more water.
Quality control standards ensure premium MgO boards keep absorption rates at or below 0.34% by weight. This feature helps the boards handle tough environmental conditions without losing their structural properties.
ASTM G21 Mold Resistance: 0/0/0 Rating for MgO
Mold resistance is another key factor when choosing building materials. The standard ASTM G21 test checks how well plastic products and polymeric materials resist fungi. MgO boards score a perfect 0/0/0 rating, which means they completely resist mold growth.
This excellent performance comes from several protective features:
1.Inorganic composition: MgO boards are made mostly of minerals that don't support fungal growth
2.Naturally antimicrobial properties: The material stops mold, mildew, fungus, and rot
3.Low moisture retention: Minimal water absorption prevents mold spores from growing
Lab tests confirm these properties. MgO sheathing works well without vapor barriers in all climate zones. The boards' internal moisture stays below what microbes need to grow, no matter how humid it gets outside.
Wood-based products like plywood contain cellulose and lignin - food for fungi. That's why they're prone to mold growth. MgO boards stay mold-free throughout their life without needing chemical treatments.
25-Day Drying Time for Plywood vs 4 Days for MgO
Drying time after getting wet matters a lot in real-life building situations. Lab tests show magnesium oxide boards dry completely in about four days after full saturation. Plywood and OSB take almost 25 days to get back to normal moisture levels.
This quick-drying advantage means:
Construction can restart sooner after rain
Less chance of moisture getting trapped in walls
Lower risk of damage to nearby materials
Less time for mold to develop while drying
Field tests back up these lab results. MgO boards keep their shape after getting wet, with no swelling, warping, or coming apart. They keep almost 100% of their bending strength after 25 wet/dry cycles. Plywood loses 9% strength and gypsum gets 36-52% weaker under the same conditions.
MgO boards resist water well but aren't waterproof. Direct water exposure for more than an hour might cause some expansion. In spite of that, properly installed MgO panels work better than traditional sheathing in real-life moisture challenges, especially in bathrooms, kitchens, and other humid spaces.
Structural Strength and Impact Resistance Benchmarks
Tests show MgO boards work better than regular floor sheathing materials. The numbers tell us why these panels work so well when you need something tough that can handle heavy loads.
Flexural Strength: 15–22 MPa in MgO Boards
The way a material bends under weight tells us a lot about how well it will hold up. Good quality MgO boards can flex without breaking, with strength ratings between 15 MPa and 22 MPa across their width. They're even stronger lengthwise, reaching up to 30 MPa.
Here's what these numbers mean in the ground:
| Material |
Flexural Strength |
What This Means |
| MgO Board |
15-22 MPa |
Stays strong under heavy loads |
| OSB/Plywood |
Variable (lower) |
More likely to sag |
| Gypsum |
Much lower |
Cracks when stressed |
MgO's high flexural strength comes from its unique makeup and how it's made. The bonds between magnesium and oxygen atoms create crystals that spread out the stress through the whole panel. This makes MgO boards perfect for places where things get loaded and unloaded over and over.
Shear Strength: 280 psf with Single Fastener
Shear strength shows how well materials handle parallel forces - crucial for floors and walls. Half-inch MgO sheathing can handle more than 280 psf, and some top-end products go up to 350 psf.
Let's look at how well it holds fasteners:
One #10-13 pancake head screw in MgO sheathing can hold more than 155 lbs
The industry only asks for 32 lbs - this is a big deal as it means that MgO is much stronger
Builders love this strong grip on fasteners. They can attach cladding right to MgO sheathing without reaching back to the frame. This makes building faster and stronger.
This means you get:
Fewer materials needed
Easier construction
Better stability
Fasteners that stay put
Better protection against wind and earthquakes
Impact Resistance: >5 KJ/m² in High-Traffic Areas
Impact resistance shows how well something takes a hit without breaking - vital in busy areas. MgO boards can take hits above 5 KJ/m² without much damage. Top-quality MgO panels can even handle more than 20 KJ/m² in special uses.
MgO boards work great in tough spots like:
Busy hallways and stairs
Commercial spaces that need to last
Schools and hospitals that take a beating
Walls that see heavy use
These tough panels last longer and cost less to maintain. Regular drywall gets dented, cracked, and punched through with normal use. MgO panels stay strong even in rough conditions.
These strength numbers aren't just specs on paper. MgO boards work better than old-school materials in every way that counts. They last longer, go up faster, and keep working year after year in real-life applications.
Environmental and Health Impact Comparison
Magnesium oxide boards are a game-changer in construction. These boards offer eco-friendly advantages over traditional building materials. The manufacturing process, lifecycle effects, and zero harmful substances make them a greener choice to build sustainably.
73% Lower CO2 Emissions than Portland Cement
MgO production creates fewer greenhouse gasses compared to traditional Portland cement. The calcination process needs temperatures between 700-1000°C, which is a big deal as it means that it's much lower than the 1500°C needed for Portland cement. This temperature difference leads to much less energy use in manufacturing.
The emissions savings tell a compelling story:
MgO cements produce only 0.5-0.6 tons of net CO2 per ton
This shows a 40-50% reduction compared to Portland cement
Some MgO formulations can absorb CO2 throughout their lifecycle
MgO boards achieve greater environmental benefits through carbon mineralization. The higher portion of reactive oxides in the binder system enables CO2 absorption. The cement industry produces about 8% of all human-made CO2 emissions. Switching to MgO-based materials could help reach climate goals faster.
Recyclability and Cradle-to-Cradle Lifecycle
MgO panels are eco-friendly from production to disposal. Traditional gypsum board waste faces strict landfill regulations. MgO boards, however, follow cradle-to-cradle principles:
They're recyclable at end-of-life, reducing landfill waste
Raw materials come from minerals, not forest products
Magnesite (MgCO3) needs no chemical processing
Some types are "Nutritional Waste" that boost soil health
The raw materials boost sustainability. Magnesium is the eighth most abundant element in Earth's crust and third most common mineral in seawater. Resource depletion isn't a concern with MgO production.
MgO board recycling helps reduce construction waste. Lifecycle assessment (LCA) studies show MgO structural insulated panels are more eco-friendly than conventional options. Their resistance to moisture and mold means they last longer, making them even more environmentally sound.
No VOCs, Formaldehyde, or Silica in MgO Boards
MgO boards are a healthier choice. These panels are free from:
Formaldehyde
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
Asbestos materials
Crystalline silica
Ammonia or benzene
Heavy metal salts
Hexavalent chromium
These boards are exceptional for health-sensitive spaces. Building occupants breathe cleaner air since the boards don't release harmful gasses or chemicals. Installation is safer too - cutting MgO sheathing doesn't require OSHA-approved respirators, unlike silica-containing materials.
If you have respiratory sensitivities, MgO boards are a great choice because they're allergen and irritant-free. They achieve a perfect 0/0/0 rating in ASTM G21 mold resistance testing. This makes them ideal for people with allergies, asthma, or chemical sensitivities.
The boards stay non-toxic throughout their lifespan. Under fire conditions, they produce almost no smoke or toxic emissions. This is unlike traditional materials that release harmful compounds when exposed to heat or flames.
Cost Analysis and Long-Term ROI
Builders need to look beyond technical specifications when they invest in magnesium oxide boards. These boards show impressive performance, and understanding their cost dynamics helps make smarter decisions about this advanced material.
Upfront Cost: $1.50–$3.50/sq ft for MgO vs $0.50–$2.50 for Plywood
MgO boards cost between $1.50 to $3.50 per square foot. Traditional plywood proves cheaper at $0.50 to $2.50 per square foot. Standard drywall remains the most budget-friendly option at $0.30 to $0.70 per square foot. The price difference stems from MgO panels' advanced material composition and superior features.
Maintenance Savings from Mold and Pest Resistance
Building expenses follow a predictable pattern. Construction costs make up just 10-20% of lifetime expenses. Maintenance and operations take up the remaining 80-90%. MgO boards need minimal repairs throughout their life cycle and save money through:
Lower moisture and impact damage repairs
Zero mold removal costs
Fewer replacements needed in high-traffic or damp areas
10-Year ROI: Reduced Repairs and Insurance Premiums
MgO boards' long-term financial benefits outweigh their higher upfront costs. Buildings with magnesium oxide panels qualify for lower insurance premiums due to their fire resistance. These panels cut insurance costs by providing budget-friendly fire-rated wall assemblies with NFPA 285 approved systems.
MgO boards keep their structural integrity without deterioration, warping, swelling, or delamination in harsh weather. Innovation MgO Wall Panels can stay fully exposed up to six months during construction while carrying a 10-year limited product warranty. This feature significantly reduces weather-related replacement costs.
Conclusion
MgO boards are the best choice for modern construction projects compared to traditional floor sheathing materials. The test results we got into show how MgO performs better in all critical areas.
Fire safety is MgO boards' most impressive feature. These boards don't burn even at temperatures above 780°C and have a zero flame spread rating. This gives them a huge safety advantage. Regular plywood burns quickly in fires, but MgO gives people four times longer to evacuate in emergencies.
The water and mold resistance of MgO technology is nowhere near what traditional materials offer. With just 0.34% water absorption and a perfect 0/0/0 mold resistance rating, these panels stay strong even in wet conditions. On top of that, MgO boards dry five times faster than plywood after getting wet. This means fewer delays and less damage during construction.
Test results prove MgO's structural strength. The boards show flexural strength of 15-22 MPa, great shear strength, and impact resistance above 5 KJ/m². This creates floors and walls that handle heavy loads well and resist daily wear.
Environmental benefits make an even stronger case to use MgO. The manufacturing process creates 73% less CO2 than Portland cement. The boards don't contain harmful chemicals like VOCs or formaldehyde and can be recycled completely. This makes them a great fit for sustainable construction.
MgO boards cost more at first ($1.50-$3.50/sq ft compared to plywood's $0.50-$2.50), but their longer life and lower maintenance are worth it. Building owners save money through fewer repairs, lower insurance costs, and less frequent replacements.
The test results show why more construction professionals choose MgO technology for tough jobs. MgO boards aren't just another option - they represent real progress in floor sheathing materials. Builders who want better performance in challenging conditions will without doubt benefit from this remarkable material.
 BMSC 517 New Sulfate MgO Board
BMSC 517 New Sulfate MgO Board Multi-Support MgO Wall Sheathing Board
Multi-Support MgO Wall Sheathing Board Perseverance MgO Wall Sheathing Board
Perseverance MgO Wall Sheathing Board Multi-Support MgO Subfloor Sheathing Board
Multi-Support MgO Subfloor Sheathing Board Perseverance MgO Subfloor Sheathing Board
Perseverance MgO Subfloor Sheathing Board MagMatrix MgO Underlayment Panel/board
MagMatrix MgO Underlayment Panel/board


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español





