Sulfate MgO Board, often referred to as magnesium oxide board, has become a popular choice in modern construction and interior finishing due to its combination of fire resistance, moisture resistance, and durability. However, one of the questions many builders, architects, and homeowners have is: how well does Sulfate MgO Board handle impact or mechanical stress? Understanding this aspect is crucial, especially in high-traffic areas or locations where walls and surfaces may be subjected to daily wear, knocks, or accidental impacts.
1. Understanding Sulfate MgO Board
Sulfate MgO Board is manufactured using magnesium oxide (MgO) as a primary binder, often combined with magnesium chloride, fillers, and reinforcing fibers. Its structure provides a rigid, high-strength surface that is resistant to moisture and fire. The inclusion of natural fibers or synthetic reinforcements in some boards can further improve its resistance to cracking and breakage.
The composition of Sulfate MgO Board gives it a few inherent advantages in handling impact:
- High compressive strength: The board can bear considerable weight without deformation.
- Dimensional stability: It maintains shape under changes in humidity or temperature.
- Surface hardness: Its surface resists scratches and minor abrasions.
However, like any rigid panel material, it does have limitations, especially under direct impact or concentrated mechanical stress.
2. Mechanical Properties of Sulfate MgO Board
Several mechanical properties determine how a material responds to stress:
- Flexural Strength: Flexural or bending strength measures how much force a board can withstand before it bends or cracks. Sulfate MgO Board typically has a flexural strength of around 8–15 MPa, depending on thickness and manufacturer. This makes it stiffer than standard gypsum board but less flexible than some fiber cement boards.
- Impact Resistance: Impact resistance is a measure of how well the board can absorb energy from a sudden blow. Standard Sulfate MgO Boards generally perform well against minor impacts such as knocks from furniture or door handles, but severe impacts, like a heavy object thrown against the wall, may cause cracking or chipping.
- Compressive Strength: This measures the board’s ability to withstand direct pressure. Sulfate MgO Board can bear significant weight vertically, which is why it is often used in wall and ceiling applications where load-bearing performance is moderately important.
- Tensile Strength: While the board has good compressive strength, its tensile strength (resistance to being pulled apart) is lower, which is typical for cementitious boards. Reinforced boards with fibers can improve this characteristic.
Understanding these mechanical properties helps architects and engineers determine where Sulfate MgO Board can be safely installed and where additional reinforcement might be necessary.
3. Factors Affecting Impact Resistance
The ability of Sulfate MgO Board to withstand mechanical stress depends on several factors:
3.1 Board Thickness
Thicker boards generally offer better resistance to impact. A 12mm or 15mm board will absorb energy from a blow better than a 6mm or 9mm panel. Thinner boards are more susceptible to cracking under direct stress.
3.2 Mounting and Framing
How the board is installed greatly affects its performance. A board mounted on closely spaced studs or joists distributes force more evenly, reducing the likelihood of localized cracking. In contrast, wide stud spacing can leave panels unsupported, making them more vulnerable to impact.
3.3 Reinforcement
Some Sulfate MgO Boards include fiberglass mesh or natural fibers, which improve both tensile strength and impact resistance. Reinforced boards can better resist denting or cracking from sudden stress.
3.4 Environmental Conditions
Humidity and temperature changes can affect the board’s mechanical properties. While Sulfate MgO Board is moisture-resistant, prolonged exposure to water or high humidity may slightly reduce its strength, making it more vulnerable to mechanical stress.
3.5 Edge Treatment
The edges of a board are typically the weakest point. Boards with tapered or reinforced edges can better resist chipping or cracking when subjected to impact near corners or joints.
4. Real-World Performance Under Impact
In practical applications, Sulfate MgO Board shows reliable performance in most indoor environments:
- Residential Walls: It withstands normal knocks and bumps from furniture, doors, and household items without visible damage.
- High-Traffic Areas: In schools, offices, or corridors, boards may require additional protection, such as corner beads or wall guards, to prevent chipping.
- Ceilings: Sulfate MgO Board installed on ceilings handles weight from light fixtures and minor vibrations well, though careful installation is required to prevent sagging.
- Bathrooms and Kitchens: Impact resistance is coupled with water resistance, making it superior to traditional gypsum boards in wet areas, though heavy impacts can still cause cracks.
It is worth noting that while Sulfate MgO Board performs well against distributed or moderate impact, sharp or heavy concentrated forces, like dropping a hammer or moving heavy equipment, may still damage the board. This is why installation guidelines often recommend reinforcement in high-risk areas.
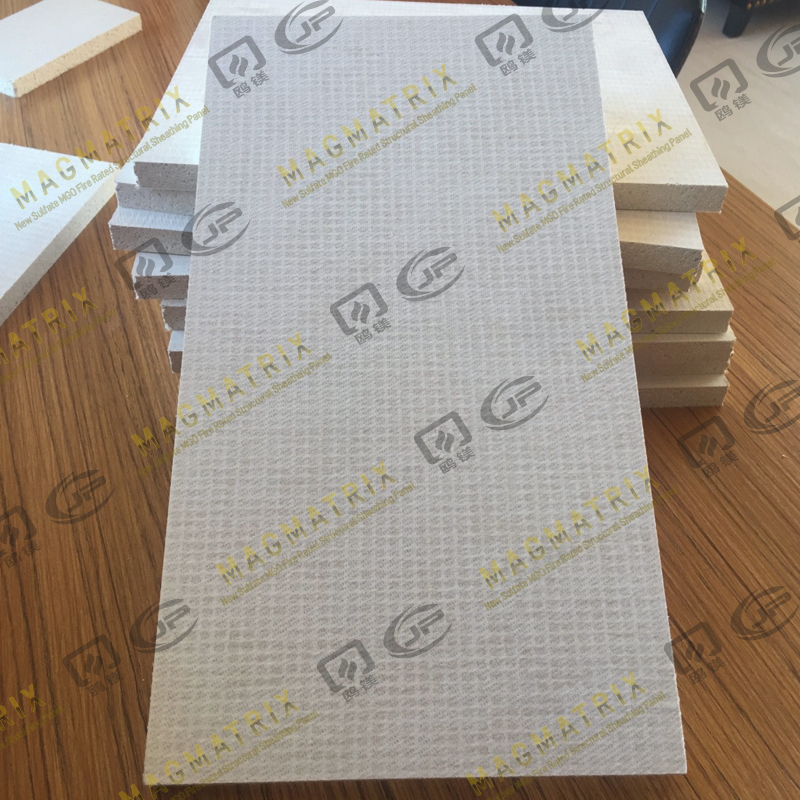

5. Comparisons With Other Boards
Understanding how Sulfate MgO Board handles mechanical stress is easier when compared to other common materials:
| Material |
Flexural Strength |
Impact Resistance |
Notes |
| Gypsum Board |
5–7 MPa |
Low |
Susceptible to dents and cracks |
| Fiber Cement Board |
10–18 MPa |
High |
Excellent impact resistance; heavier and harder to cut |
| Sulfate MgO Board |
8–15 MPa |
Medium-High |
Balanced strength, fire-resistant, moisture-resistant |
| Plywood |
15–20 MPa |
Medium |
Flexible and resilient, prone to moisture damage if untreated |
From the table, it’s evident that Sulfate MgO Board provides better impact resistance than gypsum but may not match heavy-duty fiber cement boards in areas with extremely high mechanical stress. Its strength is, however, sufficient for most residential, commercial, and light industrial applications.
6. Tips for Maximizing Impact Performance
To ensure Sulfate MgO Board performs optimally under mechanical stress:
- Use the Appropriate Thickness: Match board thickness to the application and expected level of impact.
- Proper Framing: Keep stud spacing consistent and follow manufacturer guidelines for support.
- Reinforce Vulnerable Areas: Install corner beads, skirting, or protective panels in high-traffic areas.
- Avoid Sharp Impacts: Educate occupants or workers about potential damage from heavy or pointed objects.
- Regular Maintenance: Inspect boards periodically for hairline cracks and repair them promptly to prevent spreading.
- Finish Application: Paint or skim coating can provide a minor protective layer and improve surface resilience.
By combining correct installation practices with awareness of the board’s limits, users can ensure Sulfate MgO Board maintains structural and aesthetic integrity for years.
7. Case Studies and Practical Observations
Several real-world observations highlight the board’s behavior:
- Schools and Play Areas: Sulfate MgO Board has been successfully used in classrooms, corridors, and locker rooms. While occasional dents occur from balls or furniture, the board rarely cracks fully, especially when reinforced.
- Commercial Buildings: In offices, reception areas, and lobbies, the board provides a durable surface capable of handling chairs, trolleys, and minor collisions without damage.
- Wet and Humid Areas: Bathrooms, kitchens, and laundry areas benefit from the board’s moisture resistance; however, impact protection may require additional finishing, such as ceramic tiles or wall panels.
These observations indicate that Sulfate MgO Board can effectively balance durability, fire resistance, and moisture resistance, making it a versatile choice.
8. Limitations and Considerations
Despite its advantages, there are a few limitations:
- High-Impact Zones: Areas prone to heavy knocks, like gymnasiums or industrial zones, may require stronger boards or additional protective measures.
- Edge Vulnerability: Corners and edges are prone to chipping if unprotected.
- Transportation and Handling: Boards must be handled carefully during delivery and installation to avoid cracking from bending or dropping.
By understanding these constraints, designers and builders can plan installations that maximize the board’s strengths while mitigating risks.
Conclusion
Sulfate MgO Board offers a practical solution for construction projects that require moderate to high durability under impact or mechanical stress. Its combination of flexural strength, surface hardness, and dimensional stability makes it more resilient than traditional gypsum boards and suitable for a variety of environments. While it is not impervious to all forms of mechanical stress, proper selection of thickness, reinforcement, and installation techniques can greatly enhance its performance.
For architects, builders, and homeowners, recognizing the strengths and limits of Sulfate MgO Board ensures that walls, ceilings, and panels remain functional and aesthetically pleasing, even in areas subject to daily wear and impact.
In conclusion, Sulfate MgO Board provides a balanced, reliable, and practical option for modern construction, particularly where a combination of impact resistance, fire safety, and moisture resistance is desired. Careful installation and reinforcement in high-risk areas further optimize its performance, ensuring that it continues to meet the demands of real-world usage for years to come.
 BMSC 517 New Sulfate MgO Board
BMSC 517 New Sulfate MgO Board Multi-Support MgO Wall Sheathing Board
Multi-Support MgO Wall Sheathing Board Perseverance MgO Wall Sheathing Board
Perseverance MgO Wall Sheathing Board Multi-Support MgO Subfloor Sheathing Board
Multi-Support MgO Subfloor Sheathing Board Perseverance MgO Subfloor Sheathing Board
Perseverance MgO Subfloor Sheathing Board MagMatrix MgO Underlayment Panel/board
MagMatrix MgO Underlayment Panel/board


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español





